Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Perrone et al. (2018)¶
A tutorial on how to build a surrogate model based on OpenML data as done for Scalable Hyperparameter Transfer Learning by Perrone et al..
Publication¶
This example demonstrates how OpenML runs can be used to construct a surrogate model.
In the following section, we shall do the following:
Retrieve tasks and flows as used in the experiments by Perrone et al. (2018).
Build a tabular data by fetching the evaluations uploaded to OpenML.
Impute missing values and handle categorical data before building a Random Forest model that maps hyperparameter values to the area under curve score.
# License: BSD 3-Clause
import openml
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
from sklearn.compose import ColumnTransformer
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
flow_type = "svm" # this example will use the smaller svm flow evaluations
The subsequent functions are defined to fetch tasks, flows, evaluations and preprocess them into a tabular format that can be used to build models.
def fetch_evaluations(run_full=False, flow_type="svm", metric="area_under_roc_curve"):
"""
Fetch a list of evaluations based on the flows and tasks used in the experiments.
Parameters
----------
run_full : boolean
If True, use the full list of tasks used in the paper
If False, use 5 tasks with the smallest number of evaluations available
flow_type : str, {'svm', 'xgboost'}
To select whether svm or xgboost experiments are to be run
metric : str
The evaluation measure that is passed to openml.evaluations.list_evaluations
Returns
-------
eval_df : dataframe
task_ids : list
flow_id : int
"""
# Collecting task IDs as used by the experiments from the paper
# fmt: off
if flow_type == "svm" and run_full:
task_ids = [
10101, 145878, 146064, 14951, 34537, 3485, 3492, 3493, 3494,
37, 3889, 3891, 3899, 3902, 3903, 3913, 3918, 3950, 9889,
9914, 9946, 9952, 9967, 9971, 9976, 9978, 9980, 9983,
]
elif flow_type == "svm" and not run_full:
task_ids = [9983, 3485, 3902, 3903, 145878]
elif flow_type == "xgboost" and run_full:
task_ids = [
10093, 10101, 125923, 145847, 145857, 145862, 145872, 145878,
145953, 145972, 145976, 145979, 146064, 14951, 31, 3485,
3492, 3493, 37, 3896, 3903, 3913, 3917, 3918, 3, 49, 9914,
9946, 9952, 9967,
]
else: # flow_type == 'xgboost' and not run_full:
task_ids = [3903, 37, 3485, 49, 3913]
# fmt: on
# Fetching the relevant flow
flow_id = 5891 if flow_type == "svm" else 6767
# Fetching evaluations
eval_df = openml.evaluations.list_evaluations_setups(
function=metric,
tasks=task_ids,
flows=[flow_id],
uploaders=[2702],
output_format="dataframe",
parameters_in_separate_columns=True,
)
return eval_df, task_ids, flow_id
def create_table_from_evaluations(
eval_df, flow_type="svm", run_count=np.iinfo(np.int64).max, task_ids=None
):
"""
Create a tabular data with its ground truth from a dataframe of evaluations.
Optionally, can filter out records based on task ids.
Parameters
----------
eval_df : dataframe
Containing list of runs as obtained from list_evaluations()
flow_type : str, {'svm', 'xgboost'}
To select whether svm or xgboost experiments are to be run
run_count : int
Maximum size of the table created, or number of runs included in the table
task_ids : list, (optional)
List of integers specifying the tasks to be retained from the evaluations dataframe
Returns
-------
eval_table : dataframe
values : list
"""
if task_ids is not None:
eval_df = eval_df[eval_df["task_id"].isin(task_ids)]
if flow_type == "svm":
colnames = ["cost", "degree", "gamma", "kernel"]
else:
colnames = [
"alpha",
"booster",
"colsample_bylevel",
"colsample_bytree",
"eta",
"lambda",
"max_depth",
"min_child_weight",
"nrounds",
"subsample",
]
eval_df = eval_df.sample(frac=1) # shuffling rows
eval_df = eval_df.iloc[:run_count, :]
eval_df.columns = [column.split("_")[-1] for column in eval_df.columns]
eval_table = eval_df.loc[:, colnames]
value = eval_df.loc[:, "value"]
return eval_table, value
def list_categorical_attributes(flow_type="svm"):
if flow_type == "svm":
return ["kernel"]
return ["booster"]
Fetching the data from OpenML¶
Now, we read all the tasks and evaluations for them and collate into a table. Here, we are reading all the tasks and evaluations for the SVM flow and pre-processing all retrieved evaluations.
eval_df, task_ids, flow_id = fetch_evaluations(run_full=False, flow_type=flow_type)
X, y = create_table_from_evaluations(eval_df, flow_type=flow_type)
print(X.head())
print("Y : ", y[:5])
cost degree gamma kernel
5193 0.00159429241413488 NaN 181.752067498531 NaN
2464 0.192867395009426 NaN NaN linear
82 0.716338867624746 NaN NaN linear
2301 0.110931877761327 NaN NaN linear
553 0.0136743117655568 NaN 0.00333704847239886 NaN
Y : 5193 0.493294
2464 0.689505
82 0.974565
2301 0.696169
553 0.920973
Name: value, dtype: float64
Creating pre-processing and modelling pipelines¶
The two primary tasks are to impute the missing values, that is, account for the hyperparameters that are not available with the runs from OpenML. And secondly, to handle categorical variables using One-hot encoding prior to modelling.
# Separating data into categorical and non-categorical (numeric for this example) columns
cat_cols = list_categorical_attributes(flow_type=flow_type)
num_cols = list(set(X.columns) - set(cat_cols))
# Missing value imputers for numeric columns
num_imputer = SimpleImputer(missing_values=np.nan, strategy="constant", fill_value=-1)
# Creating the one-hot encoder for numerical representation of categorical columns
enc = OneHotEncoder(handle_unknown="ignore")
# Combining column transformers
ct = ColumnTransformer([("cat", enc, cat_cols), ("num", num_imputer, num_cols)])
# Creating the full pipeline with the surrogate model
clf = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=50)
model = Pipeline(steps=[("preprocess", ct), ("surrogate", clf)])
Building a surrogate model on a task’s evaluation¶
The same set of functions can be used for a single task to retrieve a singular table which can be used for the surrogate model construction. We shall use the SVM flow here to keep execution time simple and quick.
# Selecting a task for the surrogate
task_id = task_ids[-1]
print("Task ID : ", task_id)
X, y = create_table_from_evaluations(eval_df, task_ids=[task_id], flow_type="svm")
model.fit(X, y)
y_pred = model.predict(X)
print("Training RMSE : {:.5}".format(mean_squared_error(y, y_pred)))
Task ID : 145878
Training RMSE : 9.8235e-06
Evaluating the surrogate model¶
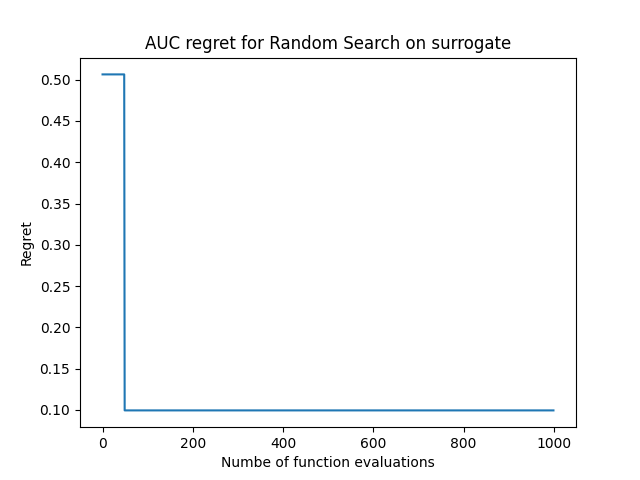
The surrogate model built from a task’s evaluations fetched from OpenML will be put into trivial action here, where we shall randomly sample configurations and observe the trajectory of the area under curve (auc) we can obtain from the surrogate we’ve built.
NOTE: This section is written exclusively for the SVM flow
# Sampling random configurations
def random_sample_configurations(num_samples=100):
colnames = ["cost", "degree", "gamma", "kernel"]
ranges = [
(0.000986, 998.492437),
(2.0, 5.0),
(0.000988, 913.373845),
(["linear", "polynomial", "radial", "sigmoid"]),
]
X = pd.DataFrame(np.nan, index=range(num_samples), columns=colnames)
for i in range(len(colnames)):
if len(ranges[i]) == 2:
col_val = np.random.uniform(low=ranges[i][0], high=ranges[i][1], size=num_samples)
else:
col_val = np.random.choice(ranges[i], size=num_samples)
X.iloc[:, i] = col_val
return X
configs = random_sample_configurations(num_samples=1000)
print(configs)
cost degree gamma kernel
0 753.083986 3.583279 50.737294 polynomial
1 355.526301 3.878007 41.679450 linear
2 932.432157 3.145557 389.464725 sigmoid
3 953.159145 4.038180 827.401051 sigmoid
4 574.413551 4.234187 163.051256 radial
.. ... ... ... ...
995 254.727697 4.246266 646.101839 polynomial
996 591.986261 2.800502 601.801761 polynomial
997 275.642334 3.442371 777.160153 radial
998 87.852844 3.368254 383.192396 radial
999 108.931212 4.528182 713.249618 linear
[1000 rows x 4 columns]
preds = model.predict(configs)
# tracking the maximum AUC obtained over the functions evaluations
preds = np.maximum.accumulate(preds)
# computing regret (1 - predicted_auc)
regret = 1 - preds
# plotting the regret curve
plt.plot(regret)
plt.title("AUC regret for Random Search on surrogate")
plt.xlabel("Numbe of function evaluations")
plt.ylabel("Regret")
Text(33.972222222222214, 0.5, 'Regret')
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 36.175 seconds)
